- 2023-08-11 15:31:38
- 9464 热度
- 0 评论
上一篇文章介绍了一些Session和Cookie的基础知识,这篇文章开始正式介绍Spring Session是如何对传统的Session进行改造的。官网这么介绍Spring Session:
Spring Session provides an API and implementations for managing a user’s session information. It also provides transparent integration with:
- HttpSession - allows replacing the HttpSession in an application container (i.e. Tomcat) neutral way. Additional features include:
- Clustered Sessions - Spring Session makes it trivial to support clustered sessions without being tied to an application container specific solution.
- Multiple Browser Sessions - Spring Session supports managing multiple users’ sessions in a single browser instance (i.e. multiple authenticated accounts similar to Google).
- RESTful APIs - Spring Session allows providing session ids in headers to work with RESTful APIs
- WebSocket - provides the ability to keep the
HttpSessionalive when receiving WebSocket messages
其具体的特性非常之多,具体的内容可以从文档中了解到,笔者做一点自己的总结,Spring Session的特性包括但不限于以下:
- 使用GemFire来构建C/S架构的httpSession(不关注)
- 使用第三方仓储来实现集群session管理,也就是常说的分布式session容器,替换应用容器(如tomcat的session容器)。仓储的实现,Spring Session提供了三个实现(redis,mongodb,jdbc),其中redis使我们最常用的。程序的实现,使用AOP技术,几乎可以做到透明化地替换。(核心)
- 可以非常方便的扩展Cookie和自定义Session相关的Listener,Filter。
- 可以很方便的与Spring Security集成,增加诸如findSessionsByUserName,rememberMe,限制同一个账号可以同时在线的Session数(如设置成1,即可达到把前一次登录顶掉的效果)等等
介绍完特性,下面开始一步步集成Spring Session
使用Redis集成Spring Session
- 引入依赖,Spring Boot的版本采用1.5.4
<dependency> |
- 配置
配置类开启Redis Http Session
@Configuration |
基本是0配置,只需要让主配置扫描到@EnableRedisHttpSession即可
配置文件application.yml,配置连接的redis信息
spring: |
- 编写测试Controller,以便于观察Spring Session的特性,和前一篇文章使用同样的代码
@Controller |
启动类省略,下面开始测试。
在浏览器中访问如下端点:http://localhost:8080/test/cookie?browser=chrome,下面是连续访问4次的结果
1 不存在session,设置browser=chrome |
如果还记得上一篇文章中运行结果的话,会发现和原生的session管理是有一些差别,原先的信息中我们记得Cookie中记录的Key值是JSESSIONID,而替换成RedisHttpSession之后变成了SESSION。接着观察redis中的变化:
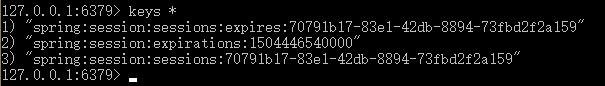
解析一下这个redis store,如果不纠结于细节,可以跳过,不影响使用。
1 spring:session是默认的Redis HttpSession前缀(redis中,我们常用’:’作为分割符)。
2 每一个session都会有三个相关的key,第三个key最为重要,它是一个HASH数据结构,将内存中的session信息序列化到了redis中。如上文的browser,就被记录为sessionAttr:browser=chrome,还有一些meta信息,如创建时间,最后访问时间等。
3 另外两个key,expirations:1504446540000和sessions:expires:7079…我发现大多数的文章都没有对其分析,前者是一个SET类型,后者是一个STRING类型,可能会有读者发出这样的疑问,redis自身就有过期时间的设置方式TTL,为什么要额外添加两个key来维持session过期的特性呢?这需要对redis有一定深入的了解才能想到这层设计。当然这不是本节的重点,简单提一下:redis清除过期key的行为是一个异步行为且是一个低优先级的行为,用文档中的原话来说便是,可能会导致session不被清除。于是引入了专门的expiresKey,来专门负责session的清除,包括我们自己在使用redis时也需要关注这一点。在开发层面,我们仅仅需要关注第三个key就行了。
总结
本节主要讲解了Spring Boot如何集成Spring Session,下一节将介绍更加复杂的特性。包括自定义Cookie序列化策略,与Spring Security的集成,根据用户名查找session等特性以及使用注意点。
- Spring(403)
- Boot(208)
- Spring Boot(187)
- Spring Cloud(82)
- Java(82)
- Cloud(82)
- Security(60)
- Spring Security(54)
- Boot2(51)
- Spring Boot2(51)
- Redis(31)
- SQL(29)
- Mysql(25)
- Dalston(24)
- IDE(24)
- mongoDB(22)
- MVC(22)
- JDBC(22)
- IDEA(22)
- Web(21)
- CLI(20)
- Alibaba(19)
- SpringMVC(19)
- Docker(17)
- SpringBoot(17)
- Git(16)
- Eclipse(16)
- Vue(16)
- JPA(15)
- Apache(15)
- ORA(15)
- Tomcat(14)
- Linux(14)
- HTTP(14)
- Mybatis(14)
- Oracle(14)
- jdk(14)
- OAuth(13)
- Nacos(13)
- Pro(13)
- XML(13)
- JdbcTemplate(13)
- JSON(12)
- OAuth2(12)
- Data(12)
- int(11)
- Myeclipse(11)
- stream(11)
- not(10)
- Bug(10)
- Hystrix(9)
- ast(9)
- maven(9)
- Map(9)
- Swagger(8)
- APP(8)
- Bit(8)
- API(8)
- session(8)
- Window(8)
- windows(7)
- too(7)
- HTML(7)
- Github(7)
- JavaMail(7)
- Cache(7)
- File(7)
- mail(7)
- IntelliJ(7)
- nginx(6)
- Server(6)
- ueditor(6)
- jar(6)
- ehcache(6)
- UDP(6)
- RabbitMQ(6)
- star(6)
- and(6)
- Excel(6)
- Log4J(6)
- pushlet(6)
- apt(6)
- read(6)
- Freemarker(6)
- WebFlux(6)
- JSP(6)
- Bean(6)
- error(6)
- are(5)
- SVN(5)
- for(5)
- DOM(5)
- Sentinel(5)
- the(5)
- JWT(5)
- rdquo(5)
- PHP(5)
- Struts(5)
- string(5)
- Syntaxhighlighter(5)

